Fracture
Fracture
What is a Fracture?
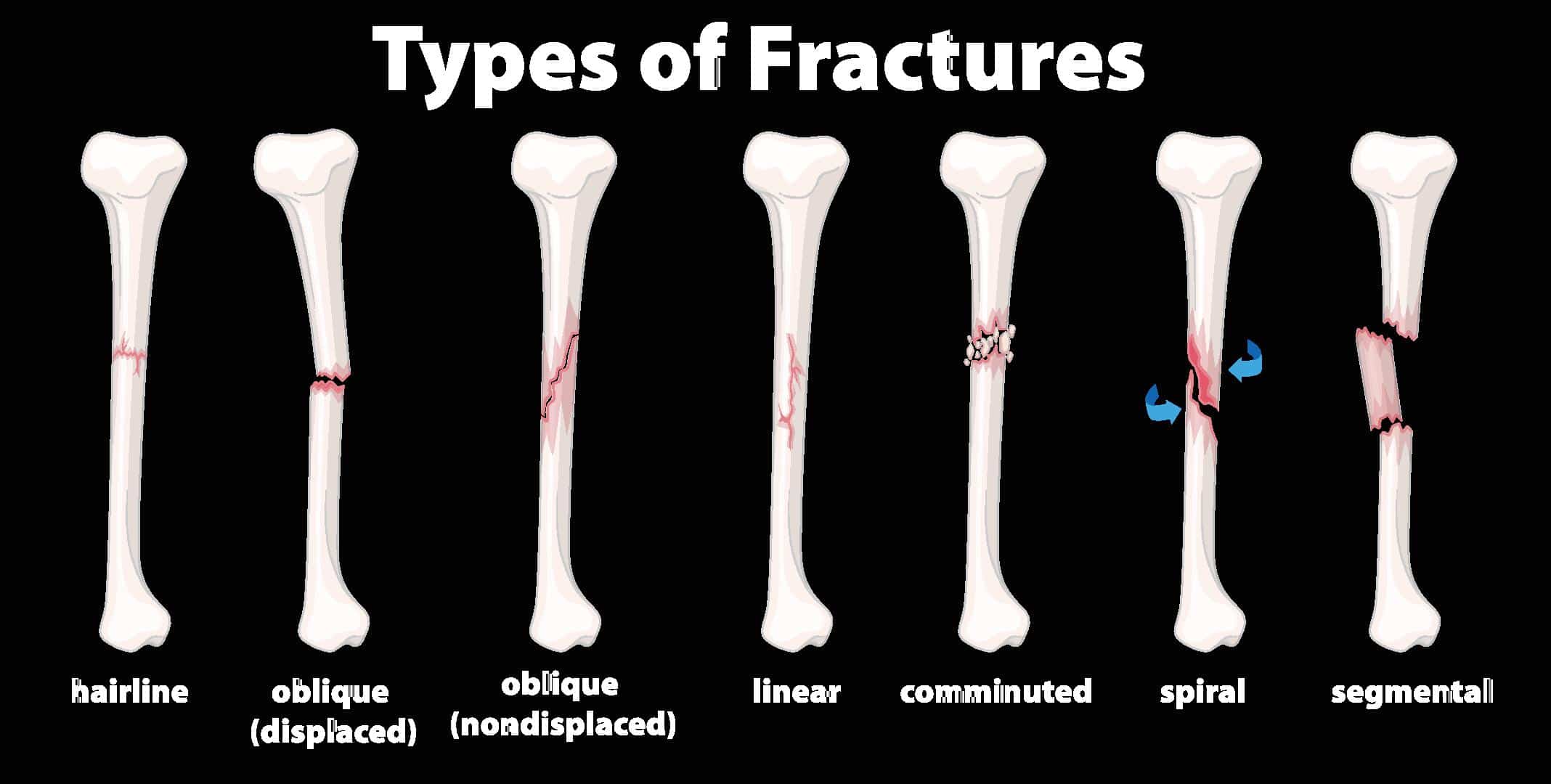
A fracture is a medical term used to describe a break or crack in a bone. The severity of fractures varies, ranging from minor hairline cracks to severe, compound fractures where the bone may pierce the skin. Depending on the location and extent, fractures require specific treatment to promote proper healing.
Types of fractures include:
- Closed Fracture: The bone is broken, but it does not puncture the skin.
- Open (Compound) Fracture: The bone breaks and punctures the skin, making it prone to infections.
- Comminuted Fracture: The bone breaks into several pieces.
- Stress Fracture: Often caused by repetitive force or overuse, especially in athletes.
- Greenstick Fracture: A partial fracture where the bone bends but does not break completely, commonly seen in children.
What Causes a Fracture?
Fractures occur for various reasons, but common causes include:
- Accidents: Falls, car accidents, and sports injuries are frequent causes of fractures.
- Osteoporosis: A condition where bones become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures, especially in older adults.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress or overuse of certain bones, particularly in athletes, can lead to stress fractures.
- Infections or Diseases: Conditions like cancer or bone infections can weaken the bones and make them more vulnerable to breaks.
- Age: As we age, our bones naturally lose density and strength, making fractures more common.
How to Identify a Fracture: Symptoms to Watch For
Common symptoms of a fracture include:
- Pain: Intense, localized pain at the site of injury, often worsening with movement.
- Swelling and Bruising: The affected area may become swollen and discolored.
- Deformity: The limb or affected area may appear out of alignment or misshapen.
- Inability to Move: Difficulty or inability to move the affected part of the body.
- Tenderness: The area surrounding the fracture may feel tender to the touch.
Diagnosing a Fracture
A medical professional will diagnose a fracture through a physical examination and medical imaging. Common diagnostic tools include:
- X-rays: The most common and effective imaging tool for identifying fractures.
- CT Scans: A more detailed image used for complex fractures.
- MRI: Typically used to examine soft tissue injuries alongside bone fractures.
Treatment Options for a Fracture
Treatment for a fracture depends on the type, location, and severity of the break. Standard treatments include:
- Casting or Splinting: For minor fractures, immobilization with a cast or splint is usually sufficient to allow the bone to heal.
- Surgical Intervention: Complex fractures may require surgery to realign the bones and insert metal plates, screws, or rods to stabilize the fracture.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications help manage pain and inflammation during the healing process.
- Physical Therapy: After the bone heals, physical therapy may be necessary to restore mobility, strength, and flexibility to the affected area.
Healing and Recovery from a Fracture
The recovery process for a fracture depends on the severity and location of the break. Here’s what to expect during recovery:
- Immobilization: The first step in healing is keeping the bone still to allow proper alignment and healing. This could involve wearing a cast, brace, or splint.
- Bone Healing: The body naturally begins to form new bone tissue to repair the fracture. This process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the fracture’s location.
- Physical Rehabilitation: Once the bone has healed, rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy are crucial for regaining strength, range of motion, and function.
- Regular Checkups: Follow-up visits with your doctor are essential to monitor the healing process and ensure there are no complications.
Complications of Fractures
While most fractures heal well with appropriate treatment, some complications can arise, including:
- Infection: Particularly in open fractures, there is a risk of infection due to bacteria entering the wound.
- Nonunion or Malunion: Sometimes, the bone does not heal properly, leading to chronic pain or deformity.
- Nerve Damage: If a fracture is near nerves, it can cause damage, resulting in numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Some fractures, especially in joints, may lead to arthritis later in life.
Preventing Fractures: How to Protect Your Bones
While you can’t prevent all fractures, taking steps to maintain strong, healthy bones can reduce your risk. Consider these tips:
- Strengthen Bones with Calcium and Vitamin D: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone health. Foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals help maintain strong bones.
- Exercise Regularly: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or strength training, can increase bone density and improve balance.
- Wear Protective Gear: In sports or high-risk activities, always wear appropriate protective equipment to minimize injury.
- Prevent Falls: For older adults, eliminating tripping hazards and using handrails in bathrooms and stairs can significantly reduce the risk of fractures from falls.
