Knee Fracture Surgery In Nagpur
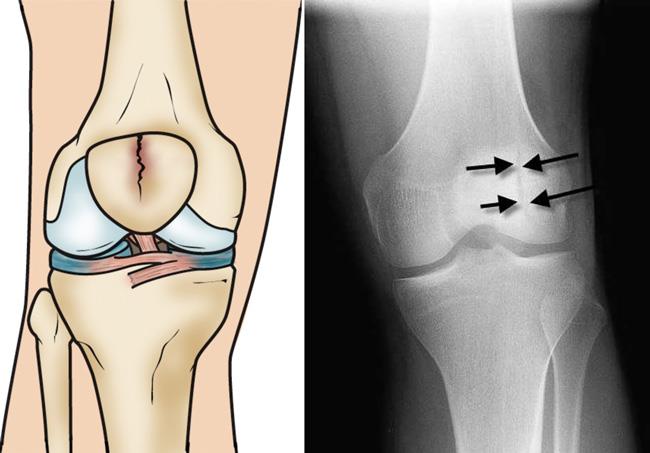
Knee Fracture Surgery In Nagpur
What Is Knee Fracture Surgery?
Knee fracture surgery is a medical procedure aimed at repairing broken bones in the knee area. The knee is a complex joint, consisting of bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, all of which work together to provide stability and movement. When a fracture occurs in the femur, tibia, or patella (kneecap), surgery may be required to:
- Realign fractured bones for proper healing
- Stabilize the knee joint to prevent further injury
- Restore function and mobility to the knee
- Minimize the risk of arthritis or long-term joint damage
When Is Knee Fracture Surgery Necessary?
Not all knee fractures require surgery. However, in more severe cases, surgery is often recommended to promote optimal healing and prevent complications. Here are situations where knee fracture surgery may be necessary:
- Displaced Fractures: When the bones are not aligned properly and need to be repositioned.
- Open Fractures: When the bone breaks through the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
- Comminuted Fractures: When the bone breaks into multiple pieces.
- Fractures with Damage to Soft Tissues: If ligaments or cartilage in the knee are also damaged, surgery may be required to repair both the bone and soft tissue.
- Inability to Heal Without Surgery: If non-surgical treatments such as casting or bracing are ineffective in promoting proper healing.
Types of Knee Fracture Surgery
The specific type of knee fracture surgery depends on the nature of the fracture. Some of the most common surgical options include:
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): In this procedure, the surgeon realigns the fractured bones and secures them with hardware such as plates, screws, or rods to ensure the bones stay in place while healing.
External Fixation: In cases of severe fractures or open fractures, external devices may be used to stabilize the knee from the outside, holding the bones in place as they heal.
Knee Arthroplasty: If the knee joint is severely damaged due to a fracture, a partial or total knee replacement may be necessary. This procedure involves removing damaged portions of the knee joint and replacing them with artificial components.
Patella Fracture Repair: In cases where the kneecap is fractured, surgery may be needed to realign and fixate the patella for proper function.
Recovery After Knee Fracture Surgery
Recovery time after knee fracture surgery can vary depending on the severity of the injury, the type of surgery performed, and your overall health.
Initial Recovery: After surgery, you may need to stay in the hospital for a short period, depending on the procedure. Pain management will be a priority, and you may be prescribed medications to control discomfort.
Physical Therapy: To regain strength and mobility in your knee, physical therapy is essential. Your therapist will guide you through exercises designed to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles around the knee, and restore function.
Weight-Bearing Restrictions: Depending on the type of fracture, you may need to avoid putting weight on the injured leg for several weeks. Gradually, you will be allowed to put more weight on your knee as it heals.
Long-Term Care: Following the initial recovery phase, it’s important to continue strengthening exercises and monitor for any signs of complications such as infection or stiffness in the knee joint.
Treatment Options for Knee Fractures
The treatment for a knee fracture depends on the type and severity of the fracture. Options include:
- Non-Surgical Treatment:
- Casting or Splinting: For mild fractures that are not displaced (bones remain in their correct position), your doctor may recommend immobilizing the knee with a cast or splint to allow the bones to heal.
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (R.I.C.E.): These methods can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Internal Fixation: If the fracture is displaced or complex, surgery may be required to realign the bones and secure them with screws, plates, or rods.
- Patella Fracture Surgery: In the case of a broken kneecap, surgery may be necessary to reassemble the pieces of the patella and stabilize the bone.
- Joint Replacement: In severe cases where the knee joint is badly damaged, partial or total knee replacement may be necessary.
Recovery from a Knee Fracture
Recovery from a knee fracture depends on the severity of the injury, the treatment used, and the individual’s overall health. General steps in recovery include:
- Rest and Rehabilitation: After surgery or immobilization, physical therapy will play a critical role in restoring strength, flexibility, and range of motion to the knee joint.
- Weight-Bearing: Your doctor will guide you on when it is safe to begin bearing weight on the affected leg, which is typically a gradual process.
- Recovery Timeline: For non-surgical fractures, recovery can take 6-8 weeks, while fractures requiring surgery may take several months to heal fully.
Potential Complications of Knee Fractures
While most knee fractures heal successfully, there can be complications, including:
- Infection: This is especially a risk if surgery is involved.
- Joint Stiffness: Some individuals may experience limited range of motion in the knee after healing.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: A knee fracture can increase the risk of developing arthritis in the joint over time.
- Delayed Healing: In some cases, fractures may take longer than expected to heal.
Preventing Knee Fractures
While some knee fractures are caused by accidents that cannot be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Strengthening Exercises: Focus on strengthening the muscles around your knee to provide better support.
- Bone Health: Ensure you are getting enough calcium and vitamin D to maintain healthy bones, especially as you age.
- Use Protective Gear: In sports, wear appropriate gear like knee pads to reduce the risk of injury.
